What is LEI?
The Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) is a 20-character alphanumeric code used to uniquely identify legally distinct entities that engage in financial transactions. It was introduced as a global standard by the G20 and the Financial Stability Board (FSB) to improve transparency and risk management in financial markets.
Required Documents for LEI Registration:
The exact documents required may vary slightly depending on the jurisdiction and the entity type, but typically you will need,
Entity Legal Name: Official name of the entity as per the legal documents.
Entity Address: Registered address of the entity.
Entity Registration Number: Such as a company registration number, if applicable.
Ownership and Control Information: Details about the ownership and control structure of the entity, including identifying information about direct and ultimate parent entities.
Legal Form and Status: Information about the legal form of the entity (e.g., corporation, partnership, trust) and its legal status.
Relationship to Other Entities: Information about the relationships between the entity being registered and any related entities.
Registration Process:
Select a LEI Issuer: Choose an organization accredited by the Global Legal Entity Identifier Foundation (GLEIF) to issue LEIs.
Fill out the Application Form: Provide the required information about your entity.
Submit Documentation: Submit the necessary documentation to support your application.
Validation: The LEI issuer will validate the information provided.
Payment: Pay the registration fee, which typically varies based on the issuer.
Issuance: Upon successful validation and payment, the LEI is issued to the entity.
LEI-Code
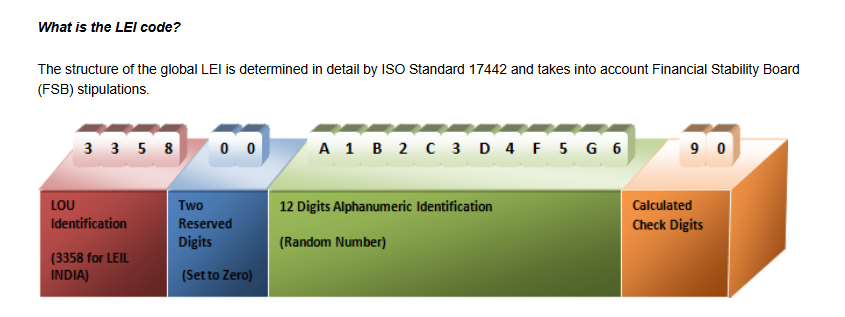
source taken RBI website
Government Official website Legal Entity Identifier India Limited
The LEI code consists of 20 characters, following the format defined by the ISO 17442 standard. It comprises four parts:
Prefix: A 4-character alphanumeric code representing the LEI issuer.
Entity Identifier: A 12-character alphanumeric code assigned by the LEI issuer to uniquely identify the legal entity.
Checksum: A 2-digit checksum used to verify the integrity of the LEI.
Example: A complete LEI might look like this: 1234ABCDE5678FGHI90.
How to Use LEI:
Regulatory Reporting: Many regulatory authorities require entities engaged in financial transactions to have an LEI for reporting purposes.
Counterparty Identification: Financial institutions and counterparties use LEIs to identify and manage risk associated with their clients.
Market Transparency: LEIs enhance market transparency by providing a standardized identification system for entities involved in financial transactions.
Risk Management: LEIs facilitate better risk management by enabling the tracking and monitoring of exposures to counterparties across different financial instruments and markets.
